Rest bus simulation scripting API
Contents
Prerequisites
Create a new project and configure the Hardware device(s) as a first step.
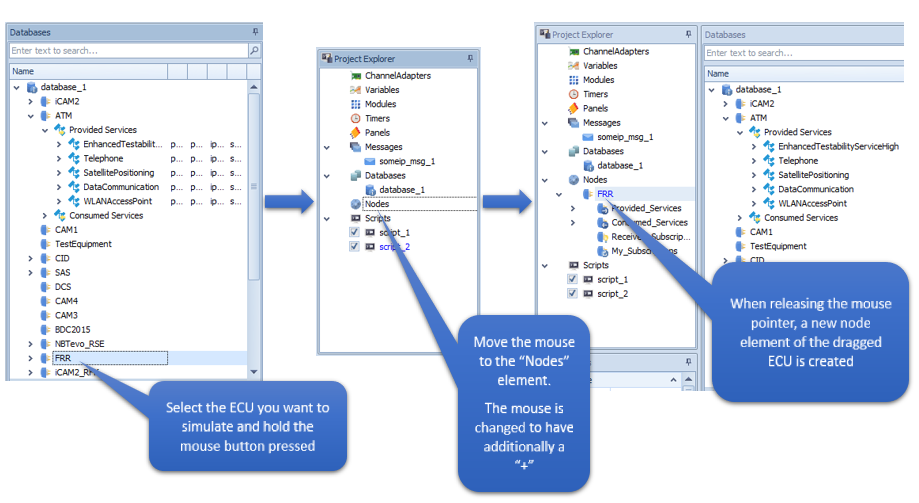
Creating ECU nodes by Drag and Drop
After adding an Ethernet database, drag and drop an ECU to the Nodes element.
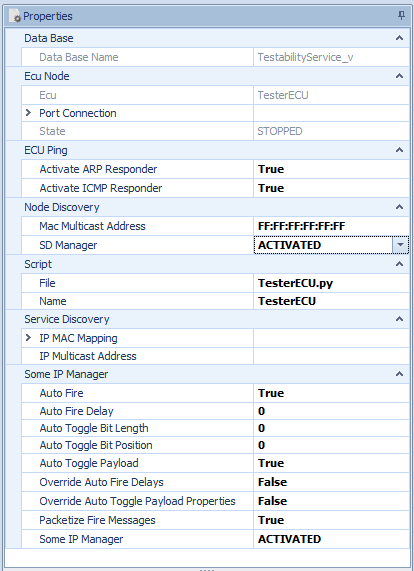
ECU Node properties
Select the created ECU node and open the Properties View to show and change the adjustments to simulate the ECU:
Ip and MAC addresses
Vlan
Used port
Activation/deactivation of
SOME/IP manager
SOME/IP-SD manager
ARP responder
ICMP responder
Use packetizing for sending SOME/IP Events
Cyclic auto fire including the delays
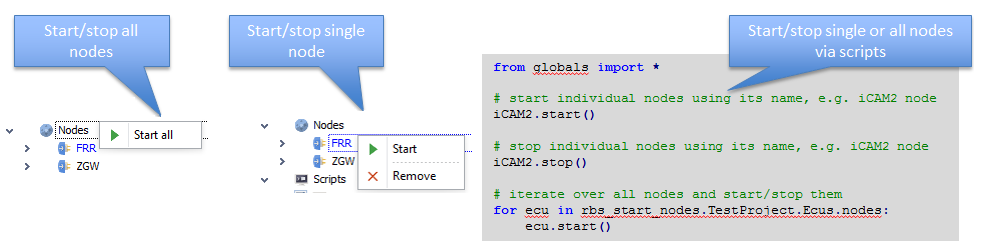
Starting and stopping ECU nodes
There are three ways on how to start and stop ECU nodes:
Start all ECU nodes via context menu of
Nodeselement.Start only one ECU node via context menu of an ECU node.
Start Nodes in scripts.
Auto fire functionality
Auto fire: Feature for sending cyclically SOME/IP events
The delay can be specified on ECU level, service level and/or event level
Priority is as follows: event > service > ecu
The activation of this feature is set only on event level via the property
Auto Fire
By default this feature is enabled
But the
Auto Fire Delayis set to 0 ms, which means deactivated
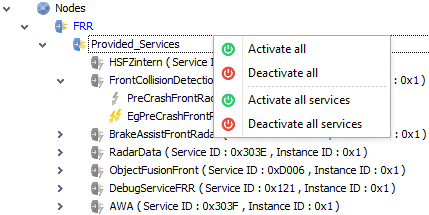
Activating and deactivation services
By default all services of the ECU node are deactivated, i.e. after the creation of a node, the user should activate the needed services. Otherwise nothing will happen when simulation is started
Each service, method, event, field and eventgroup has an
enableflag which specifies whether the element is activated or notIn order to activate everything, right click on the
providedand/ orconsumedservices element and selectActivate allActivate all
Activate all the services including its events, methods, fields and event groups
Deactivate all
De-activates all services including its events, methods, fields and event groups
Activate all services
Activates only the services without their events, etc
Deactivate all services
Deactivates all services
Properties of services, methods, events, fields and eventgroups
Each service, method, event, field and event group has further information which is read out of the Fibex file and is used during the simulation
This does not only include the timings for the startup and the main phase, but also the IP, ports, etc.
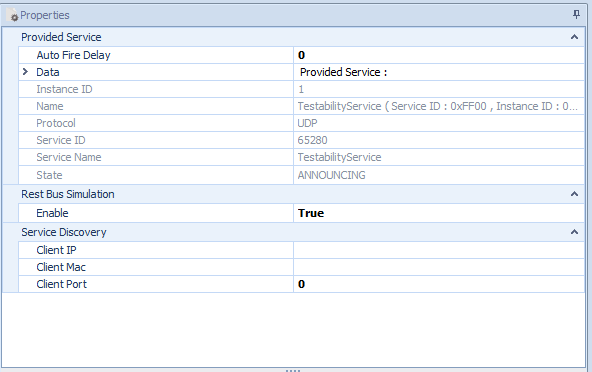
Figure 1: Service Properties
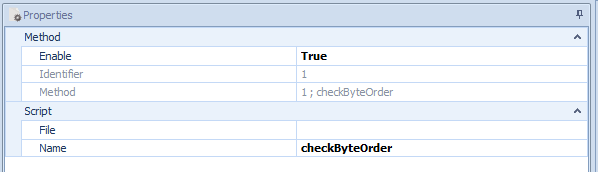
Figure 2: Method Properties
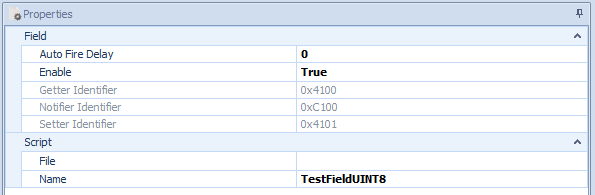
Figure 3: Field Properties
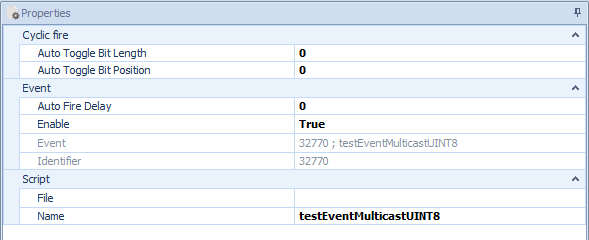
Figure 4: Event Properties
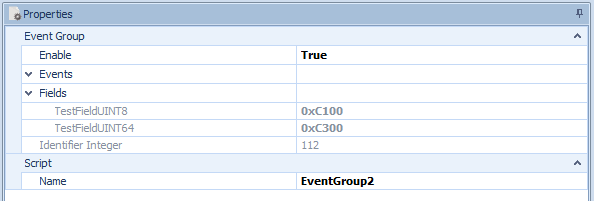
Figure 5: Event Group Properties
Example using trigger() method
from time import sleep
# enable service EnhancedTestabilityServiceHigh
ECU.enable("EnhancedTestabilityServiceHigh")
TESTER.enable("EnhancedTestabilityServiceHigh")
# enable Field InterfaceVersion
ECU.enable("EnhancedTestabilityServiceHigh.InterfaceVersion")
TESTER.enable("EnhancedTestabilityServiceHigh.InterfaceVersion")
print("Starting RBS node using the start() method")
ECU.start()
TESTER.start()
sleep(2)
print("triggering field")
ECU.trigger("EnhancedTestabilityServiceHigh.InterfaceVersion")
sleep(2)
# disable service EnhancedTestabilityServiceHigh
ECU.disable("EnhancedTestabilityServiceHigh")
TESTER.disable("EnhancedTestabilityServiceHigh")
# disable Field InterfaceVersion
ECU.disable("EnhancedTestabilityServiceHigh.InterfaceVersion")
TESTER.disable("EnhancedTestabilityServiceHigh.InterfaceVersion")
ECU.stop()
TESTER.stop()
Example using on_value_changed() method
from time import sleep
# --Functions
def on_value_changed(ecu, evt):
global serv_name, old_val, new_val
if evt.match("EnhancedTestabilityServiceHigh.InterfaceVersion"):
print(evt.service_name)
serv_name = evt.service_name
print("old value")
print(evt.old_value)
old_val = evt.old_value
print("new value")
print(evt.new_value)
new_val = evt.new_value
# Enable the service EnhancedTestabilityServiceHigh
ECU.enable("EnhancedTestabilityServiceHigh")
TESTER.enable("EnhancedTestabilityServiceHigh")
# Enable the field InterfaceVersion
ECU.enable("EnhancedTestabilityServiceHigh.InterfaceVersion")
TESTER.enable("EnhancedTestabilityServiceHigh.InterfaceVersion")
print("Starting RBS node using the start() method")
ECU.start()
TESTER.start()
sleep(2)
value = {'majorVersion': 2, 'minorVersion': 3}
TESTER.on_value_changed += on_value_changed
ECU.set_value("EnhancedTestabilityServiceHigh.InterfaceVersion", value)
ECU.trigger("EnhancedTestabilityServiceHigh.InterfaceVersion")
sleep(5)
# disable the service EnhancedTestabilityServiceHigh
ECU.disable("EnhancedTestabilityServiceHigh")
TESTER.disable("EnhancedTestabilityServiceHigh")
# disable the field InterfaceVersion
ECU.disable("EnhancedTestabilityServiceHigh.InterfaceVersion")
TESTER.disable("EnhancedTestabilityServiceHigh.InterfaceVersion")
ECU.stop()
TESTER.stop()
Example using call() method
from time import sleep
# enable service EnhancedTestabilityServiceHigh
ECU.enable('EnhancedTestabilityServiceHigh')
TESTER.enable('EnhancedTestabilityServiceHigh')
# enable method checkByteOrder
ECU.enable('EnhancedTestabilityServiceHigh.checkByteOrder')
TESTER.enable('EnhancedTestabilityServiceHigh.checkByteOrder')
print("Starting RBS node using the start() method")
ECU.start()
TESTER.start()
sleep(3)
ret = TESTER.call('EnhancedTestabilityServiceHigh.checkByteOrder', {'summandUINT8':2, 'summandUINT16':4})
print(ret)
sleep(3)
# disable service EnhancedTestabilityServiceHigh
ECU.disable('EnhancedTestabilityServiceHigh')
TESTER.disable('EnhancedTestabilityServiceHigh')
# disable field checkByteOrder
ECU.disable('EnhancedTestabilityServiceHigh.checkByteOrder')
TESTER.disable('EnhancedTestabilityServiceHigh.checkByteOrder')
ECU.stop()
TESTER.stop()
Example using on_method_called() method
# coding: utf-8
from time import sleep
def on_method_called(ecu, call):
if call.match("EnhancedTestabilityServiceLow.echoENUM"):
print(call.service_name)
print(call.request)
call.response = {'enumerationReturnElement': 'One'}
ECU.enable("EnhancedTestabilityServiceLow")
TESTER.enable("EnhancedTestabilityServiceLow")
ECU.enable('EnhancedTestabilityServiceLow.echoENUM')
TESTER.enable('EnhancedTestabilityServiceLow.echoENUM')
ECU.start()
TESTER.start()
ECU.on_method_called +=on_method_called
sleep(3)
response = TESTER.call('EnhancedTestabilityServiceLow.echoENUM', {'enumerationElement': 'Four'})
print(response)
sleep(5)
ECU.disable("EnhancedTestabilityServiceLow")
TESTER.disable("EnhancedTestabilityServiceLow")
ECU.disable("EnhancedTestabilityServiceLow.echoENUM")
TESTER.disable("EnhancedTestabilityServiceLow.echoENUM")
ECU.stop()
TESTER.stop()
Example using on_receiving() method
def on_receiving(ecu, e):
if e.protocol == "someip":
if ecu.port_connection.vlan.qinq_vlan != e.message.vlan_tag.qinq_vlan:
e.message = None
ecus = [ECU, TESTER, ECU_1, TESTER_1]
try:
for ecu in ecus:
ecu.on_receiving +=on_receiving
tc_wait_for_return()
finally:
for ecu in ecus:
ecu.on_receiving -=on_receiving