ANDi frequent use cases
Contents
Creating and sending SOME/IP-SD messages
To create a SOME/IP-SD message you have to follow this approach:
1. Perform mapping of channels to adapters
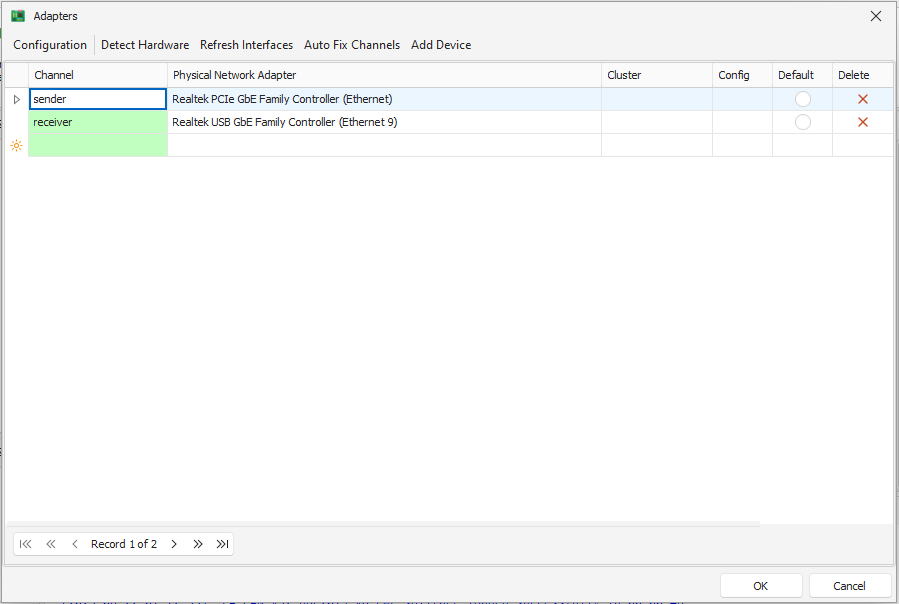
Click on adapters in the Scripting toolbar
The configuration dialog appears
Map the channels to the adapters
2. Create message object
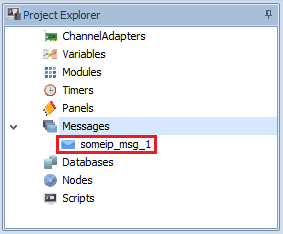
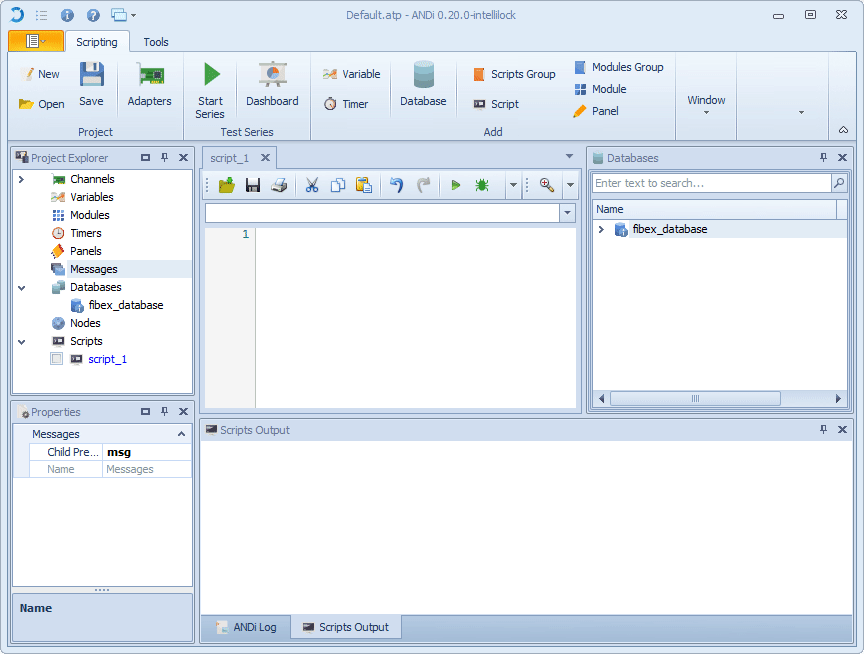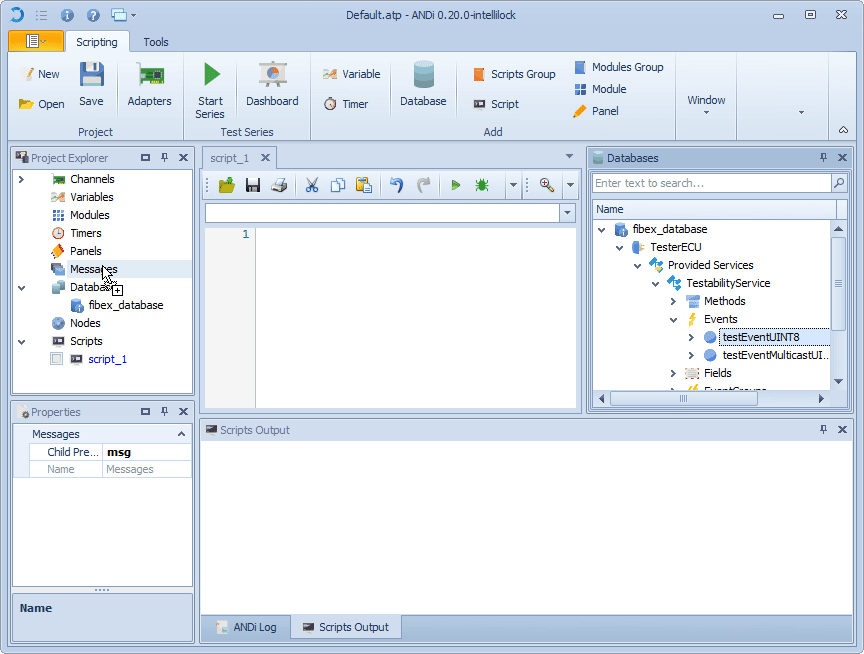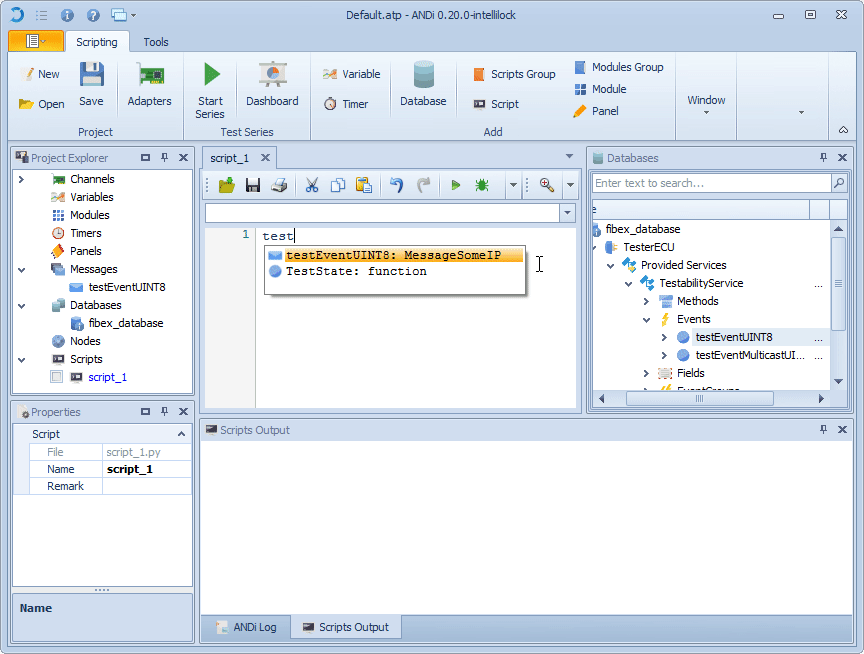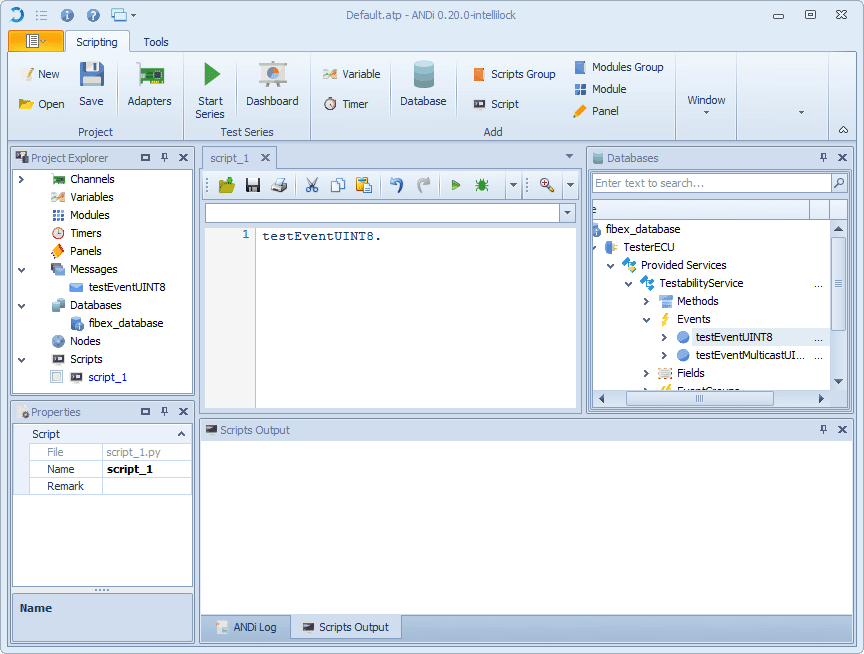
Right click on Messages
Select message to be added
3. Create Script
Right click on Scripts
Select Add Script
Open the Script in the editor and configure the message
Send message object
from globals import *
# set ethernet and ip header
someip_msg_1.ethernet_header.mac_address_source = "11:22:33:44:55:66"
someip_msg_1.ip_header.ip_address_source = "160.48.199.55"
someip_msg_1.ethernet_header.mac_address_destination = "99:88:77:66:55:44"
someip_msg_1.ip_header.ip_address_destination = "160.48.199.66"
# set SOME/IP specific fields
someip_msg_1.someip_header.service_identifier = 0x1111
someip_msg_1.someip_header.method_identifier = 0x2222
someip_msg_1.someip_header.interface_version = 0x02
someip_msg_1.someip_header.protocol_version = 0x03
someip_msg_1.someip_header.request_id = 0x4444
# set payload of SOME/IP message
someip_msg_1.payload = System.Array[Byte]([0x11,0x22,0x33])
# send the message
someip_msg_1.send()
Creating and sending messages via Drag and Drop
1. Load a Fibex database file
2. In the Messages view select an event
Move the mouse with the still pressed button to
Messagesof the Scripting view (global or local)Now release the mouse button
A new message object is then created
3. The message object can be used in the scripts
Receiving packets
import time
# dynamically create SOME/IP-SD packet
msg_someip_sd = message_builder.create_someip_sd_message("channel_01", "channel_01")
# callback function invoked on each incoming SOME/IP-SD packet
def on_msg_received(msg):
# do logic here
print(msg)
pass
# register callback function
msg_someip_sd.on_message_received += on_msg_received
# start live capturing for SOME/IP-SD packets
msg_someip_sd.start_capture()
# sleep for 5 seconds
time.sleep(5)
# de-register callback function
msg_someip_sd.on_message_received -= on_msg_received
# stop capturing
msg_someip_sd.stop_capture()
Executing and stopping scripts
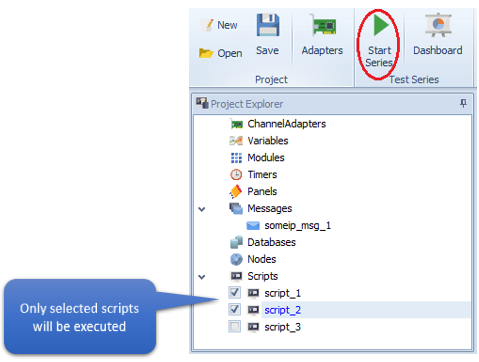
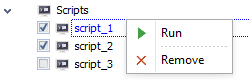
There are several ways on how to execute and stop scripts
1. Start/Stop button of the main menu
Select scripts which should be executed
Press on the Start/Stop button
2. Right click on the script name
3. Start/Stop button of the editor
Cyclic procedures using timers
Timers can be used in order to implement cyclic procedures
Timer events:
on_time_elapsed(source, current_date)
The interval attribute of the timer specifies the cycle time of the timer
After expiration of the interval the on_time_elapsed() event is invoked and the registered callback functions are executed
on_time_out(source, current_date)
When starting the timer the running time of the timer can be optionally specified
After expiration of the given running time the on_time_out event is triggered and the registered callback functions are executed
Timer methods:
Start()
Start(timeout_ms)
Stop()
Reset ()
Note
registered callback functions are executed in separated threads.
In fact, one should make sure that the callback function does not require more execution time than the specified interval time. Otherwise, they can be overlapped!
Cyclic sending of a SOME/IP Event
from globals import *
import time
msg_someip.ethernet_header.mac_address_destination = "d8:18:2b:80:19:be"
msg_someip.ethernet_header.mac_address_source = "38:06:b4:80:03:52"
msg_someip.ip_header.ip_address_destination ="160.48.199.16"
msg_someip.ip_header.ip_address_source = "160.48.199.93"
msg_someip.transport_header.port_destination = 30501
msg_someip.transport_header.port_source = 30501
msg_someip.someip_header.service_identifier = 0xb512
msg_someip.someip_header.method_identifier = 0x01
msg_someip.someip_header.protocol_version = 0x01
msg_someip.someip_header.interface_version = 0x01
msg_someip.someip_header.message_type = MessageType.REQUEST
msg_someip.someip_header.return_code = ReturnCode.E_OK
msg_someip.payload = System.Array[Byte]([0x0c, 0x04, 0x5d])
def on_time_elapsed(a,b):
msg_someip.send()
g_timer_2.on_time_elapsed += on_time_elapsed
g_timer_2.interval = 1000
g_timer_2.start()
time.sleep(5)
g_timer_2.stop()
g_timer_2.on_time_elapsed -= on_time_elapsed
Packetized SOME/IP packets
SOME/IP message objects support the creation of messages containing several SOME/IP frames (=packetized)
msg_someip_1.append_message(msg_someip_2)addsmsg_someip_2tomsg_someip_1
Packetized SOME/IP packets can be accessed and analyzed separately:
msg_someip.messages()returns a list of the SOME/IP frames which are contained in themsg_someipmessage
Sending of Packetized SOME/IP Frames
from globals import *
# set ethernet and ip header
someip_msg_1.ethernet_header.mac_address_source = "11:22:33:44:55:66"
someip_msg_1.ip_header.ip_address_source = "160.48.199.55"
someip_msg_1.ethernet_header.mac_address_destination = "99:88:77:66:55:44"
someip_msg_1.ip_header.ip_address_destination = "160.48.199.66"
# set SOME/IP specific fields
someip_msg_1.someip_header.service_identifier = 0x1111
someip_msg_1.someip_header.method_identifier = 0x2222
someip_msg_1.someip_header.interface_version = 0x02
someip_msg_1.someip_header.protocol_version = 0x03
someip_msg_1.someip_header.request_id = 0x4444
# set payload of SOME/IP message 1
someip_msg_1.payload = System.Array[Byte]([0x11,0x22,0x33])
# set SOME/IP specific fields of message 2
msg_someip_1.someip_header.service_identifier = 0x3333
msg_someip_1.someip_header.method_identifier = 0x4444
msg_someip_1.someip_header.interface_version = 0x02
msg_someip_1.someip_header.protocol_version = 0x03
msg_someip_1.someip_header.request_id = 0x5555
# set payload of SOME/IP message 2
msg_someip_1.payload = System.Array[Byte]([0x44,0x55,0x66])
# append SOME/IP message 2 to SOME/IP message 1
someip_msg_1.append_message(msg_someip_1)
# send the message 1
someip_msg_1.send()
Receiving Packetized SOME/IP Frames
from globals import *
# returns the payload as a list
def get_int_list(system_bytes):
result = []
for s in system_bytes:
result.append(hex(int(s)))
return result
# stores the current SOME/IP frame
someip_frame = 0
def on_msg_received(msg):
global someip_frame
# loop over contained SOME/IP frames contained in received SOME/IP message
for m in msg.messages:
someip_frame += 1
print("[{0}] 0x{1:x}".format(someip_frame, m.someip_header.message_id))
print("[{0}] {1}".format(someip_frame, get_int_list(m.payload)))
# add on_msg_received method as listener
msg_someip.on_message_received += on_msg_received
# Capturing from a pcap file, second parameter means synchronous
msg_someip.start_capture(someip_empfangen_paketized.TestProject.DirectoryName + "\\pcap\\someip_paketized_one_packet.pcap",True)
# clean up
msg_someip.on_message_received -= on_msg_received
msg_someip.stop_capture()
Adding SOME/IP-SD Entries
SOME/IP-SD messages provide several methods for adding entries to the message
Two categories
Using another entry
Specifying each field of the entry
SOME/IP-SD with several Entries
msg_someip_sd = message_builder.create_someip_sd_message("channel_01", "channel_01")
msg_someip_sd.add_find_service_entry(0x1111,0x01,0x01,0x01,0x01)
msg_someip_sd.add_offer_service_entry(0x2222,0x01,0x01,0x01,0x01)
msg_someip_sd.add_subscribe_event_group_entry(0x3333,0x01,0x01,0x01,0x01)
msg_someip_sd.add_subscribe_event_group_ack_entry(0x4444,0x01,0x01,0x01,0x01)
msg_someip_sd.add_stop_offer_service_entry(0x5555,0x01,0x01,0x01,0x01)
msg_someip_sd.add_subscribe_event_group_ack_entry(0x6666,0x01,0x01,0x01,0x01)
msg_someip_sd.send()
(this packet does not respect the SOME/IP-SD requirements, since there are incompatible entries in the same packet but ANDi allows it e.g. to perform negative tests.)
Extracting SOME/IP-SD Entries
SOME/IP-SD messages provide methods for extracting the entries out of the message
Those methods return a list of the respective entry type
msg_someip_sd.get_find_service_entries()
msg_someip_sd.get_offer_service_entries()
msg_someip_sd.get_stop_offer_service_entries()
msg_someip_sd.get_subscribe_event_group_entries()
msg_someip_sd.get_subscribe_event_group_ack_entries()
msg_someip_sd.get_subscribe_event_group_nack_entries()
msg_someip_sd.get_stop_subscribe_event_group_entries()
from globals import *
# callback function, invoked on each incoming SOME/IP-SD packet
def on_msg_received(msg):
for f in msg.get_find_service_entries():
print("find service-id: {0}".format(f.service_id))
for o in msg.get_offer_service_entries():
print("offer service-id: {0}".format(o.service_id))
for so in msg.get_stop_offer_service_entries():
print("stop offer service-id: {0}".format(so.service_id))
for s in msg.get_subscribe_event_group_entries():
print("subscribe service-id: {0}".format(s.service_id))
for sa in msg.get_subscribe_event_group_ack_entries():
print("subscribe ack service-id: {0}".format(sa.service_id))
for san in msg.get_subscribe_event_group_nack_entries():
print("subscribe nack service-id: {0}".format(san.service_id))
for sse in msg.get_stop_subscribe_event_group_entries():
print("stop subscribe service-id: {0}".format(san.service_id))
# register callback function
msg_someip_sd.on_message_received += on_msg_received
# start live capturing for SOME/IP-SD packets
msg_someip_sd.start_capture(someip_sd_entries_extrahieren.TestProject.DirectoryName + "\\pcap\\someip_sd_multiple_entries.pcap", True)
# de-register callback function
msg_someip_sd.on_message_received -= on_msg_received
# stop capturing
msg_someip_sd.stop_capture()
Adding SOME/IP-SD Option
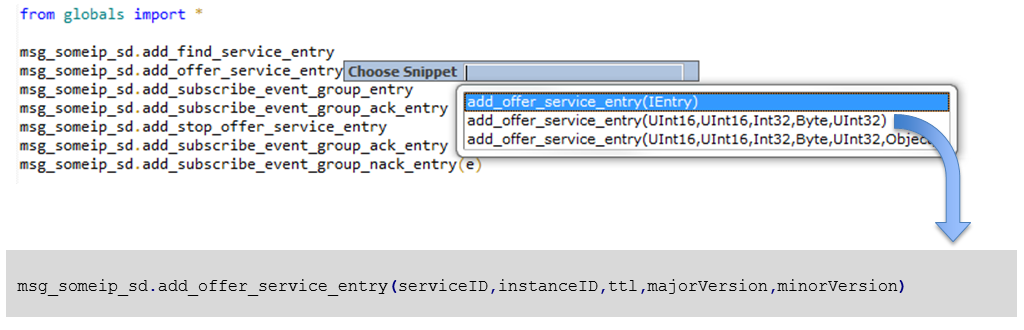
msg_someip_sd.add_ipv4_option("address",port,isUDP,isMulticast)
msg_someip_sd.add_ipv4_option(e,port,"address",isUDP,isMulticast)
msg_someip_sd.add_ipv4_option(e,port,"address",isUDP,isMulticast,index)
Currently IPv4 and IPv6 options are supported
If an entry is passed, then the options number of the entry is automatically incremented
If the options number is set wrong because of that, then this value can be set fixed in the entry
entry.flag_op_1
entry.flag_op_2
msg_someip_sd = message_builder.create_someip_sd_message("channel_01", "channel_01")
# create offer entries
o_entry_1 = msg_someip_sd.add_offer_service_entry(0x1111,0x01,0x01,0x01,0x01)
o_entry_2 = msg_someip_sd.add_offer_service_entry(0x2222,0x01,0x01,0x01,0x01)
# set number of options for second offer entry
o_entry_2.flag_op_1 = 1
# add UDP IPv4 options index and assign first and assign first offer entry
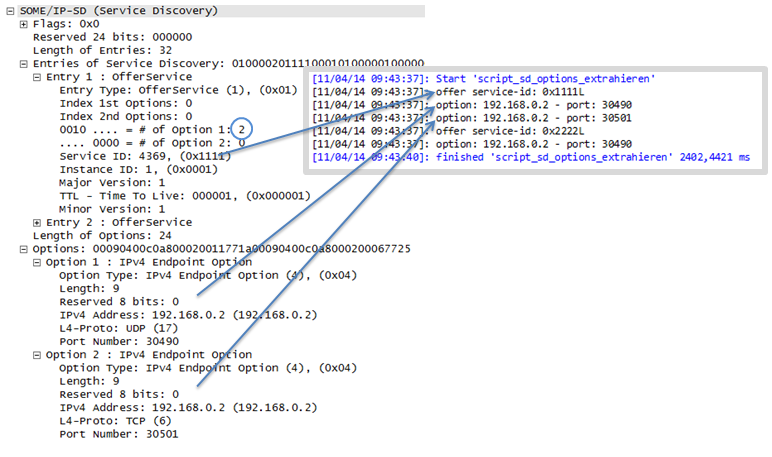
msg_someip_sd.add_ipv4_option(o_entry_1,30490,"192.168.0.2",True,False)
# add TCP IPv4 options index and assign first and assign first offer entry
msg_someip_sd.add_ipv4_option(o_entry_1,30501,"192.168.0.2",False,False)
# send message
msg_someip_sd.send()
Extracting SOME/IP-SD Option
In order to access the referenced options of an entry, one can use the "entry.options" attribute of an entry.
entry.options returns a list of options
from globals import *
# callback function, invoked on each incoming SOME/IP-SD packet
def on_msg_received(msg):
for o in msg.get_offer_service_entries():
print("offer service-id: {0}".format(hex(o.service_id)))
# iterate over all referenced options
for op in o.options:
print("option: {0} - port: {1}".format(op.ip_address, op.option_port))
# register callback function
msg_someip_sd.on_message_received += on_msg_received
# start live capturing for SOME/IP-SD packets
msg_someip_sd.start_capture(someip_sd_entries_extrahieren.TestProject.DirectoryName + "\\pcap\\someip_sd_multiple_options.pcap", True)
# de-register callback function
msg_someip_sd.on_message_received -= on_msg_received
# stop capturing
msg_someip_sd.stop_capture()
Deserializing Someip packet (payload simple parameters)
def on_msg_received(eth_msg):
if eth_msg.has_layer(PROTOCOL_TYPE.IP):
ip_layer = eth_msg.get_layer(PROTOCOL_TYPE.IP)
ip_source = ip_layer.ip_address_source
if eth_msg.has_layer(PROTOCOL_TYPE.SOMEIP) and not eth_msg.has_layer(PROTOCOL_TYPE.SOMEIP_SD):
msg_someip = eth_msg.get_someip_layer()
for msg in msg_someip.messages:
someip_layer = eth_msg.get_layer(PROTOCOL_TYPE.SOMEIP)
message_id = hex(someip_layer.someip_header.message_id).rstrip("L")
try:
print("# Trying to deserialize message_id: {0}".format(message_id))
msg.data_base = G_FIBEX_DB
dictionary_params = msg.get_input_parameters()
for param in dictionary_params:
if not param.is_complex and not param.is_array: # SIMPLE NOT ARRAY
if param.is_enum:
print("Parameter: ", param.name, ": ", param.value, "(ENUM)")
else:
print("Parameter: ", param.name, ": ", param.value, "(", param.base_data, ")")
except Exception as e:
print("[ERROR] Problem deserializing current packet")
print("{0}".format(e))
return False
Deserializing Someip packet (payload complex parameters)
def get_member(parameter, depth):
if not parameter.is_complex:
if parameter.is_enum:
return "*"*(depth -1) + ">{0} ({1}): {2} (ENUM)".format(parameter.name, parameter.base_data, parameter.value)
else:
return "*"*(depth -1) + ">{0} ({1}): {2}".format(parameter.name, parameter.base_data, parameter.value)
else:
members_string = "*"*(depth -1)
if depth > 1:
members_string += ">" + parameter.name + "< (complex)\n"
for member in parameter.members:
members_string += get_member(member, depth+1) + "\n"
return members_string
def on_msg_received(eth_msg):
if eth_msg.has_layer(PROTOCOL_TYPE.IP):
ip_layer = eth_msg.get_layer(PROTOCOL_TYPE.IP)
ip_source = ip_layer.ip_address_source
if eth_msg.has_layer(PROTOCOL_TYPE.SOMEIP) and not eth_msg.has_layer(PROTOCOL_TYPE.SOMEIP_SD):
msg_someip = eth_msg.get_someip_layer()
for msg in msg_someip.messages:
someip_layer = eth_msg.get_layer(PROTOCOL_TYPE.SOMEIP)
message_id = hex(someip_layer.someip_header.message_id).rstrip("L")
try:
print("# Trying to deserialize message_id: {0}".format(message_id))
msg.data_base = G_FIBEX_DB
dictionary_params = msg.get_input_parameters()
for param in dictionary_params:
if param.is_complex: # COMPLEX PARAM
print("Parameter: ", param.name, ": COMPLEX TYPE \n", get_member(param, 1))
except Exception as e:
print("[ERROR] Problem deserializing current packet")
print("{0}".format(e))
return False
Deserializing Someip packet (payload with array)
def get_member(parameter, depth):
if not parameter.is_complex:
if parameter.is_enum:
return "*"*(depth -1) + ">{0} ({1}): {2} (ENUM)".format(parameter.name, parameter.base_data, parameter.value)
else:
return "*"*(depth -1) + ">{0} ({1}): {2}".format(parameter.name, parameter.base_data, parameter.value)
else:
members_string = "*"*(depth -1)
if depth > 1:
members_string += ">" + parameter.name + "< (complex)\n"
for member in parameter.members:
members_string += get_member(member, depth+1) + "\n"
return members_string
def get_array_members(array_complex):
members_string = ""
for array_element in array_complex:
for el in array_element.members_objects:
parameter = el
if not parameter.is_complex:
if parameter.is_enum:
members_string += "{0} (ENUM)".format(param.value)
else:
members_string += "{0} ({1})".format(param.value, param.type)
else:
for member in el.members:
members_string += get_member(member)
return members_string
def on_msg_received(eth_msg):
if eth_msg.has_layer(PROTOCOL_TYPE.IP):
ip_layer = eth_msg.get_layer(PROTOCOL_TYPE.IP)
ip_source = ip_layer.ip_address_source
if eth_msg.has_layer(PROTOCOL_TYPE.SOMEIP) and not eth_msg.has_layer(PROTOCOL_TYPE.SOMEIP_SD):
msg_someip = eth_msg.get_someip_layer()
for msg in msg_someip.messages:
someip_layer = eth_msg.get_layer(PROTOCOL_TYPE.SOMEIP)
message_id = hex(someip_layer.someip_header.message_id).rstrip("L")
try:
print("# Trying to deserialize message_id: {0}".format(message_id))
msg.data_base = G_FIBEX_DB
dictionary_params = msg.get_input_parameters()
for param in dictionary_params:
if param.is_array: #
if param.is_complex: # ARRAY COMPLEX
print("Parameter: ", param.name, ": (ARRAY COMPLEX) ", len(param.table_complex), " elements")
for el in param.table_complex:
for member in el.members:
print(get_member(member.Value.parameter, 1))
else: # ARRAY SIMPLE
print("Parameter: ", param.name, ": (ARRAY SIMPLE)")
for array_elem in param.arrays:
for num in range(array_elem.num_elements):
print("* dimension: {0}, elem: {1} -> {2} ".format(array_elem.dimension, num, param.value[array_elem.dimension - 1 + num]))
except Exception as e:
print("[ERROR] Problem deserializing current packet")
print("{0}".format(e))
return False
Storing received data to a pcap file
from globals import *
import time
def on_time_elapsed(t,a):
# set icmp request message
msg_icmp = message_builder.create_icmp_message()
msg_icmp.type_code =ICMPv4TypeCodes1.EchoRequest
msg_icmp.ethernet_header.mac_address_source = "00:11:22:33:44:66"
msg_icmp.ethernet_header.mac_address_destination = "00:11:22:33:44:55"
msg_icmp.ip_header.ip_address_source = "192.168.2.10"
msg_icmp.ip_header.ip_address_destination = "192.168.2.11"
msg_icmp.send()
timer_1.on_time_elapsed += on_time_elapsed
adapter0.start_record(adapter_store_pcap.TestProject.DirectoryName + "\\pcap\\store_pcap_example.pcap")
timer_1.start()
time.sleep(5)
timer_1.on_time_elapsed -= on_time_elapsed
timer_1.stop()
adapter0.stop_record()
Creating messages using message_builder
Message objects can be created dynamically
For this purpose, the
message_buildermust be used.There are two types of signatures:
Passing the sender and receiver adapter
Without any parameters. In this case, the default adapter is used as sender and the receiver as adapter
Properties of the created message objects can be modified by using the API
message_builder.create_1722_message()
message_builder.create_arp_message()
message_builder.create_dhcp_message()
message_builder.create_ethernet_message()
message_builder.create_hsfz_message()
message_builder.create_icmp_message()
message_builder.create_ip_message()
message_builder.create_ptp_message()
message_builder.create_someip_message()
message_builder.create_someip_sd_message()
message_builder.create_tcp_message()
message_builder.create_tftp_message()
message_builder.create_udp_message()
message_builder.create_udp_nm_message()
Accessing properties of different layers
Setting and getting properties of a specific protocol layer requires the selection of the specific protocol layer even if it is the property of the protocol layer of the message.
Such as: setting the unicast flag of a SOME/IP-SD message.
msg_someip_sd = message_builder.create_someip_sd_message()
msg_someip_sd.ethernet_header.mac_address_source = "00:11:22:33:44:55"
msg_someip_sd.vlan_tag.vlan_priority_tag = 0x01
msg_someip_sd.ip_header.ip_address_destination ="192.168.1.3"
msg_someip_sd.transport_header.port_destination = 1234
msg_someip_sd.someip_header.client_id = 0x1234
# Select SOME/IP-SD header in order to set unicast_flag to 0x01
msg_someip_sd.someip_sd_header.unicast_flag = 0x01
Message object responding machine
from globals import *
import time
def on_time_elapsed(t,a):
# Create Ping Request
msg_icmp.type_code = ICMPv4TypeCodes1.EchoRequest
msg_icmp.ethernet_header.mac_address_source = "00:11:22:33:44:66"
msg_icmp.ethernet_header.mac_address_destination= "00:11:22:33:44:55"
msg_icmp.ip_header.ip_address_source = "192.168.2.10"
msg_icmp.ip_header.ip_address_destination= "192.168.2.11"
msg_icmp.send()
timer_1.on_time_elapsed += on_time_elapsed
def is_request(msg_src, msg_received):
if msg_received.ip_header.ip_address_destination == "192.168.2.11" and msg_received.type_code == ICMPv4TypeCodes1.EchoRequest:
return True
return False
def make_reply(msg_src, msg_received):
# Create Ping Reply
msg_src.type_code = ICMPv4TypeCodes1.EchoReply
msg_src.ip_header.ip_address_source = msg_received.ip_header.ip_address_destination
msg_src.ip_header.ip_address_destination = msg_received.ip_header.ip_address_source
msg_src.ethernet_header.mac_address_source = msg_received.ethernet_header.mac_address_destination
msg_src.ethernet_header.mac_address_destination = msg_received.ethernet_header.mac_address_source
msg_src.send()
msg_icmp= message_builder.create_icmp_message("channel_1", "channel_1")
# Register Callback Function
msg_icmp.is_request += is_request
msg_icmp.make_reply += make_reply
# Starting Responding Machine Functionality
msg_icmp.start_responding_machine()
timer_1.start()
time.sleep(5)
timer_1.stop()
msg_icmp.stop_responding_machine()
msg_icmp.is_request -= is_request
msg_icmp.make_reply -= make_reply
Handling of Fibex
ANDi provides methods for:
Getting information out of Fibex files:
ECUs
Consumed and provided services depending on: ECU Id, ECU name, IP, Instance Ids, Etc.
Events, Eventgroups and Fields
Creating Entries: Offers, Subscribes, etc.
Returned objects have in turn methods and properties to get further information
# Only a small extract of the whole list
# Use the autocompletion or the ANDi help to get all possibilities
database_1.get_all_ecus()
database_1.get_all_services()
database_1.get_consumed_event_groups(service_id,"ecu_name")
database_1.get_consumed_event_groups_by_ip(service_id,"ecu_name","ip")
database_1.get_consumed_instance_ids(service_id,"ecu_name")
database_1.get_consumed_instance_ids_by_ip(service_id,"ecu_name","ip")
database_1.get_consumed_services("ecu_name",service_id)
database_1.get_consumed_services_by_ecu_id("ECUID")
database_1.get_consumed_services_by_ecu_ip("ecu_name","ip")
database_1.get_consumed_services_by_ecu_name("ECUNAME")
database_1.get_consumed_services_by_ip("ecu_name","ip",service_id)
database_1.get_ecus_by_ip("ip")
database_1.get_ecu_by_identifier("id")
database_1.get_ecu_by_name("name")
database_1.get_eventgroups_by_service(ServiceID)
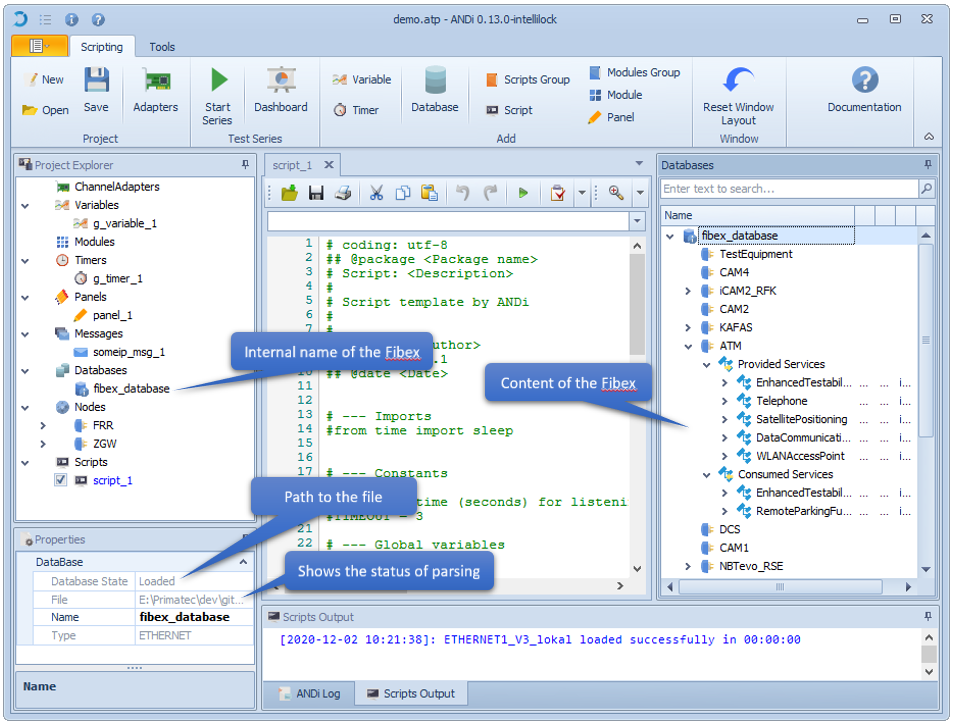
Loading Fibex
One project can load and make use of several Fibex files
Properties of the Fibex file can be inspected and changed in the Properties View: Name,File path
After ANDi has parsed the Fibex files completely, all contained ECUs and provided and consumed services can be viewed in the Messages View
Scripts can make use of the loaded Fibex files using the provided API and referencing the Fibex files via the specified name
Getting consumed and provided services
from globals import *
dict_consumed_and_provided_services = {}
# Get all ECUs contained in fibex
for e in database_1.get_all_ecus():
key = (e.ecu_name, e.ecu_id)
# Insert key, if not already contained
if key not in dict_consumed_and_provided_services:
dict_consumed_and_provided_services[key] = {}
# Get provided services
dict_provided_services = {}
for p in e.provided_services:
service = p.service
# Store services using service_id as key and service name as value
dict_provided_services[service.service_id] = service.name
# Get consumed services
dict_consumed_services = {}
for c in e.consumed_services:
service = c.service
# Store services using service_id as key and service name as value
dict_consumed_services[service.service_id] = service.name
# Store information
dict_consumed_and_provided_services[key]["provided"] = dict_provided_services
dict_consumed_and_provided_services[key]["consumed"] = dict_consumed_services
# Iterate over all ECUs stored previously
for ecu_name, ecu_id in dict_consumed_and_provided_services:
#Calculate amount of services
amount_provided = len(dict_consumed_and_provided_services[(ecu_name, ecu_id)]["provided"])
amount_consumed = len(dict_consumed_and_provided_services[(ecu_name, ecu_id)]["consumed"])
print("ecu name: {0}, provided: {1}, consumed: {2}".format(ecu_name, amount_provided, amount_consumed))
Accessing methods, fields, events and eventgroups
Services can contain methods, events, fields and eventgroups, whereas events and fields can be referenced by an eventgroup
Thus, those information can only be accessed via the service
from globals import *
# get all consumed services by 'ECUName'
for s in database_1.get_consumed_services_by_ecu_name("ECUName"):
# iterate over all event groups and print its associated events and fields
for eg in s.service.event_groups:
for e in eg.events:
print("event: {0}".format(e))
for f in eg.fields:
print("field: {0}".format(f))
# iterate over all methods of the service interface and print it out
if s.service.methods:
for m in s.service.methods:
print("method: {0}".format(m))
# all events defined in the service interface
if s.service.events:
for e in s.service.events:
print("event in si: {0}".format(e))
Further access to the properties of methods, fields, events and eventgroups is possible.
Accessing Input and Output parameters of a method
Getting the Input and Output parameters of a method is done using
input_parametersrespectivelyoutput_parametersThose properties return a list of
parameterobjects
from globals import *
# get all consumed services by 'ECUName'
for s in database_1.get_consumed_services_by_ecu_name("ECUName"):
if s.service.methods:
for m in s.service.methods:
print("method: {0}".format(m))
if m.input_parameters:
print("inputs")
for i in m.input_parameters:
print(i)
if m.return_parameters:
print("outputs")
for i in m.return_parameters:
print(i)
Sending diagnose messages
# --- Imports
from time import sleep
# --- Constants
## HSFZ port
HSFZ_PORT_SRC = 7811
HSFZ_PORT_DST = 6811
## the ECU diagnose source address
DIAG_SOURCE_ADDR = 0xF4
## the ECU diagnose target address
DIAG_TARGET_ADDR = 0x10
_src_ip = sender.get_ip()
print("sender ip : {}".format(sender.get_ip()))
_src_mac = sender.get_mac()
print("sender mac : {}".format(sender.get_mac()))
_dst_ip = receiver.get_ip()
print("receiver ip : {}".format(receiver.get_ip()))
_dst_mac = receiver.get_mac()
print("receiver mac : {}".format(receiver.get_mac()))
# --- Global variables
my_hsfz_msg_received = False
## Message used to send the HSFZ connect and disconnect requests
def on_msg_received(msg):
global my_hsfz_msg_received
print("message received ----------------------------")
print(msg.ToString())
if msg.ip_header.ip_address_source == _src_ip and\
msg.ip_header.ip_address_destination == _dst_ip:
my_hsfz_msg_received = True
print(msg.hsfz_payload)
print("---------------------------------------------")
##################################################################
# TEST CASE START #
##################################################################
######TEST BODY
# --- Pre initializations
hsfz_msg = message_builder.create_hsfz_message("sender","sender")
msg_hsfz_listener = message_builder.create_hsfz_message("sender","sender")
if hsfz_msg:
msg_hsfz_listener.ip_header.ip_address_destination = _src_ip
msg_hsfz_listener.on_message_received += on_msg_received
#create listener for TCP clients through the receiver network adapter.
msg_hsfz_listener.start_listener()
print("Server OK")
if not hsfz_msg.connected:
# Set source and destination IP addresses
hsfz_msg.ip_header.ip_address_source = _src_ip
hsfz_msg.ip_header.ip_address_destination = _dst_ip
# Set ports
hsfz_msg.transport_header.port_source = HSFZ_PORT_SRC
hsfz_msg.transport_header.port_destination = HSFZ_PORT_DST
# Set control word
hsfz_msg.ctr_word = HSFZCtrlWordMapping.CTRLWORD_REQUEST_RESPONSE
# Set diag addresses
hsfz_msg.diag.source_address = DIAG_SOURCE_ADDR
hsfz_msg.diag.target_address = DIAG_TARGET_ADDR
# Set payload (SVK_LESEN = "F1 01")
payload = System.Array[Byte](bytearray.fromhex("F1 01"))
hsfz_msg.diagnostic_payload_data = payload
# Create conennexion through the sender
hsfz_msg.connect()
print("Client Connected")
print(hsfz_msg.get_hex_bytes())
# Send HSFZ message
hsfz_msg.send()
print("Message sent")
sleep (2)
#***************************************************#
msg_hsfz_listener.stop_listener()
if my_hsfz_msg_received:
tc_return_success('My hsfz msg received')
else:
tc_return_failure('My hsfz msg not received')
else:
tc_return_failure('Failed creating hsfz message')
SOME/IP get_input_param and set_input_param
channel = "eth"
# create and configure someip message
someip_msg = message_builder.create_someip_message(channel, channel)
someip_msg.someip_header.service_identifier = service_id
someip_msg.someip_header.method_identifier = method_id
# link to the correspondent database
someip_msg.data_base = data_base
# set input parameter inBOOL to 1
someip_msg.set_input_param("inBOOL", 0x01)
# get input parameter inBOOL
param = someip_msg.get_input_param("inBOOL")
# prints 1
print(param)
# set input parameter inBOOL to 5
someip_msg.set_input_param("inBOOL", 5)
# prints 5
print(someip_msg.get_input_param("inBOOL"))