Map logical channel to a Network Adapter
Ethernet Adapter
An Ethernet adapter, also known as a Network Interface Card, is a hardware component that enables a computer to connect to a wired network. It facilitates the transmission and reception of data over Ethernet, which is the most common Local Area Network technology.
Definition of Ethernet or network loop
A network loop happens when data can travel in a circle between two or more devices because there are multiple active paths.
Purpose of Ethernet Adapters in Simulation
Ethernet traffic simulation is performed by connecting two Ethernet adapters on the same machine, creating what is known as an Ethernet loop.
Ip configuration representations
In the following image, we present the network connections for both ETH-Sender and ETH-Receiver. The naming of each adapter may differ.
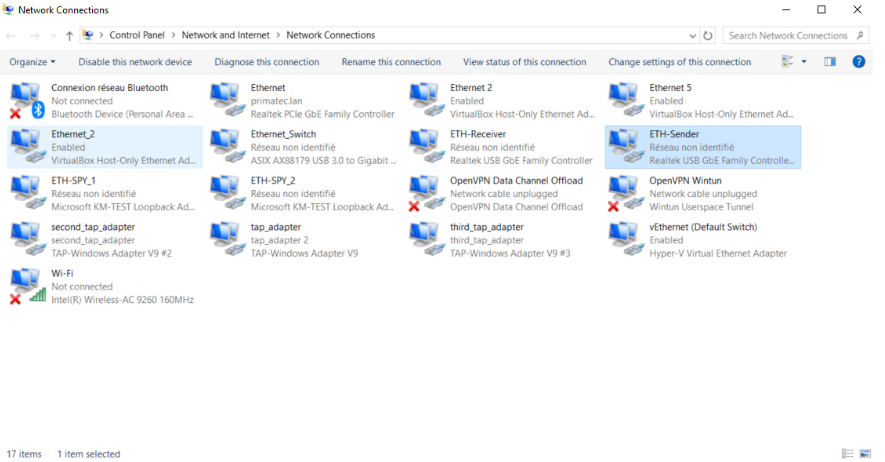
As it is shown, An IP configuration is needed for both Ethernet adapters. IP addresses need to be within the same range.
Ip configuration for ETH-Sender
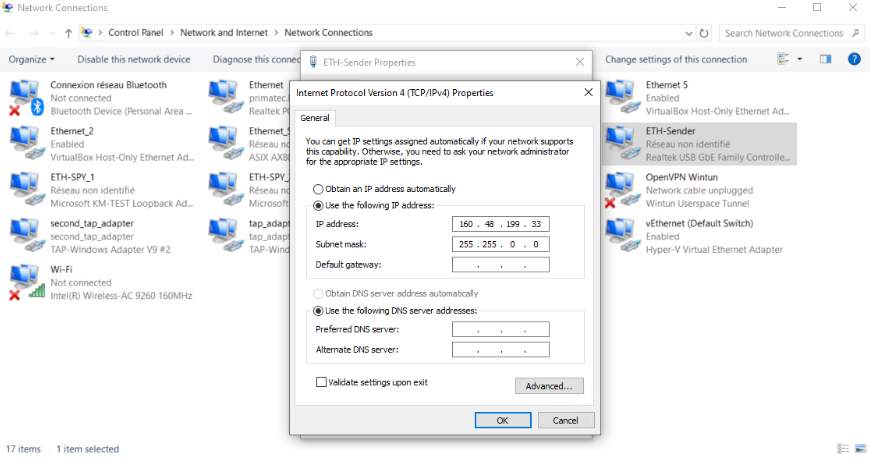
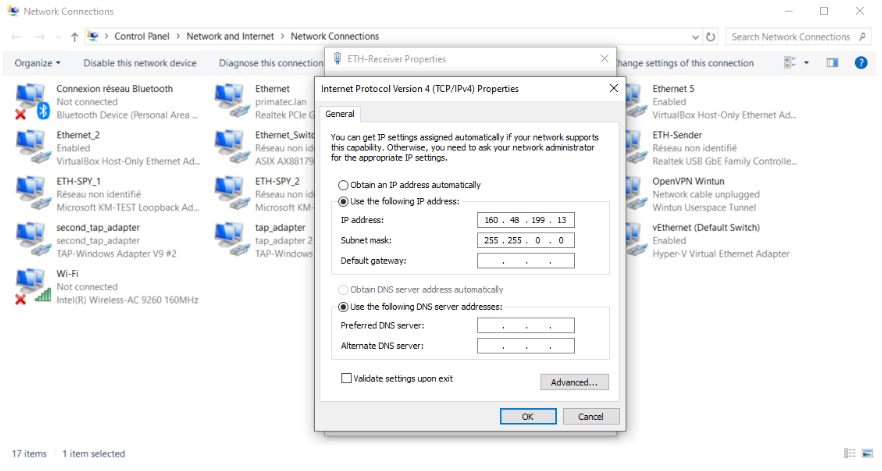
Ip configuration for ETH-Receiver
Wiring YAML configuration
The corresponding YAML configuration according to this wiring could be like this:
Channels:
ETH_Sender:
Id: 92
Type: ETHERNET
ETH_Receiver:
Id: 93
Type: ETHERNET
FrameworkConfig:
EthernetConfig:
AppLayerPorts:
SomeIp: [30501]
Mappings:
PCAP:
1:
Adapter:
Name: ETH_Sender
FriendlyName: "ETH-Sender"
BufferSize: 1024
BpfFilter: ""
Timeout: 1
TimeStampPrecision: Nanosecond
TimeStampSource: TimeStampAdapter
ImmediateMode: false
SnapshotLength: 65536
PcapDeviceMode: promiscuous
UseDataLoggerTimeStamp: false
RemoveDataLoggerMetaData: false
DataLoggerType: TECMP
LoggingActive: true
PacketProcessingActive: true
PacketIdentificationActive: true
TECMPPacketizationActive: true
CMPacketizationActive: true
2:
Adapter:
Name: ETH_Receiver
FriendlyName: "ETH-Receiver"
BufferSize: 1024
BpfFilter: ""
Timeout: 1
TimeStampPrecision: Nanosecond
TimeStampSource: TimeStampAdapter
ImmediateMode: false
SnapshotLength: 65536
PcapDeviceMode: promiscuous
UseDataLoggerTimeStamp: false
RemoveDataLoggerMetaData: false
DataLoggerType: TECMP
LoggingActive: true
PacketProcessingActive: true
PacketIdentificationActive: true
TECMPPacketizationActive: true
CMPacketizationActive: true
Example of Test case
from test_base import TestBase
from mtf.mtf_base import MtfBase
mtf_base = MtfBase()
from time import sleep
from xtr import logging, Severity
logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)
from mtf.proto_common import EthProtocolType
from mtf.enum_types import BusType
# Create the test case class, that inherits from the preset TestBase class.
class TestCaptureEthernetFrames(TestBase):
# Create setUp() method.
def setUp(self):
logger.info("Setup test case")
# Create the tearDown() method.
def tearDown(self):
logger.info("Tear down test case")
# Create the test case method that holds the main test steps.
def test_capture_ethernet_frames(self):
"""
Test the transmission of a SOME/IP message
and then verify that it was received correctly
by checking the listener's queue
"""
#create and start the listener to capture SOME/IP messages
listener = self.bus_manager.ethernet_listener(
bus_name="ETH_Receiver",
protocol=EthProtocolType.IS_SOME_IP)
listener.start_listening()
#SOME/IP properties in hexadecimal
service_id = '0101'
method_id = '8005'
some_ip_length = '0000000d'
client_id = '0000'
session_id = '0000'
some_ip_version = '01'
interface_version = '01'
message_type = '02' #refers to NOTIFICATION
return_code = '00' #refers to E_OK
payload = '0100000000'
#concatenate SOME/IP properties to get the SOME/IP payload
someip_msg_payload = ( service_id + method_id + some_ip_length +
client_id + session_id + some_ip_version +
interface_version + message_type + return_code + payload
)
msg = self.bus_manager.create_ethernet_message(
EthProtocolType.IS_SOME_IP)
#add the SOME/IP payload to the created ethernet message
msg.set_bytes(bytearray.fromhex(someip_msg_payload))
#transmit the ethernet message that contains the SOME/IP payload
self.bus_manager.bus_transmitter(BusType.ETHERNET).transmit_frame("ETH_Sender",list(msg.get_all_bytes()))
sleep(1)
#stop listening
listener.stop_listening()
#get the queue of SOME/IP captured messages
messages = listener.get_queue()
self.assertTrue(len(messages) == 1, Severity.BLOCKER,
"*** Failure: SOME/IP message is not captured")
for someip_message in messages:
#get the someip_header from the someip message
someip_header = someip_message['someip_message'].someip_header
#the expected values are hex str values we need to convert them to hex int values
self.assertTrue(int(some_ip_length, 16) == someip_header.length, Severity.BLOCKER,
"*** Failure: SOME/IP length is incorrect")
self.assertTrue(int(client_id, 16) == someip_header.client_id, Severity.BLOCKER,
"*** Failure: SOME/IP client_id is incorrect")
self.assertTrue(int(session_id, 16) == someip_header.session_id, Severity.BLOCKER,
"*** Failure: SOME/IP session_id is incorrect")
self.assertTrue(someip_header.message_type.ToString() == 'NOTIFICATION', Severity.BLOCKER,
"*** Failure: SOME/IP message_type is incorrect")
self.assertTrue(someip_header.return_code.ToString() == 'E_OK', Severity.BLOCKER,
"*** Failure: SOME/IP return_code is incorrect")